Data Governance for Healthcare: Challenges, Benefits, Core Capabilities, and Implementation
Data governance in healthcare is a standardized and structured approach to collecting, managing, analyzing, and sharing medical data transparently while adhering to ethical and regulatory standards.
Effective data governance ensures that healthcare data is managed, protected, and used efficiently, leading to improved patient outcomes, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Governance – Start Product Tour
Let’s explore why data governance is crucial in healthcare, its benefits, and how to implement it effectively.
Table of contents #
- The need for data governance in healthcare
- The benefits of data governance in healthcare
- How to implement data governance in healthcare: Essential capabilities
- Data governance in healthcare: Set the stage for high-quality patient care
- Related reads
The need for data governance in healthcare: 3 barriers to ensuring high-quality patient care #
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the COVID–19 pandemic exposed long-standing data governance issues, such as intellectual property rights, data sharing, interoperability, reuse, and storage.
The three major challenges healthcare enterprises face when data governance is lacking include:
- Inconsistent and inaccurate patient data
- Regulatory compliance risks
- Data sharing and interoperability
1. Inconsistent and inaccurate patient data #
Without data governance, patient information can become fragmented across different systems, leading to inconsistencies and inaccuracies.
For example, a hospital might have patient records stored in multiple systems—EMRs, lab systems, and billing systems—without a unified view.
As a result, accessing comprehensive patient information becomes difficult, increasing administrative workload with tasks such as manual data entry, reconciliation, and scouring through disparate data sources.
2. Regulatory compliance risks #
Healthcare organizations must comply with stringent regulations for data storage and reuse. Inefficient storage and reuse practices increase costs and result in data being used inappropriately or without proper consent, raising compliance issues.
Non-compliance can attract hefty fines and reputational damage. Let’s look at the requirements of such healthcare-specific regulations and their implications.
Regulation of healthcare data in the US: HIPAA #
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) of 1996 mandates privacy protection for healthcare data in the United States. It applies to all entities handling health-related information, including developers of healthcare applications for the US market.
Non-compliance with HIPAA can result in significant fines. For example, in 2014, the New York-Presbyterian Hospital and Columbia University were fined $4.8 million for a breach that made thousands of patients’ electronic protected health information (ePHI) accessible online. This breach highlighted the importance of conducting risk analyses and implementing proper safeguards.
Similarly, in 2017, Oklahoma State University – Center for Health Sciences (OSU-CHS) was fined $875,000 for multiple HIPAA violations, including delays in breach reporting and failure to perform a risk analysis.
Regulation of healthcare data in the EU: GDPR #
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), effective since 2018, governs the handling of EU citizens’ personal data globally. This regulation has significant implications for healthcare applications that collect data from EU citizens, requiring stringent data security measures and respect for user privacy rights.
GDPR violations also lead to hefty fines. In 2021, the French Lead Supervisory Authority (LSA) fined Dedalus Biologie, a medical software company, 1.5 million euros for GDPR non-compliance. The company failed to implement adequate security measures, such as data encryption and proper authentication processes, leading to a health data breach.
3. Data sharing and interoperability #
The Health Data Collaborative highlights interoperability as one of the biggest challenges in using health data to optimize patient outcomes.
Healthcare data comes in various formats and from numerous sources, such as electronic health records (EHRs), medical devices, health surveys, clinical trials, and more. This data is held in silos by the entities collecting them.
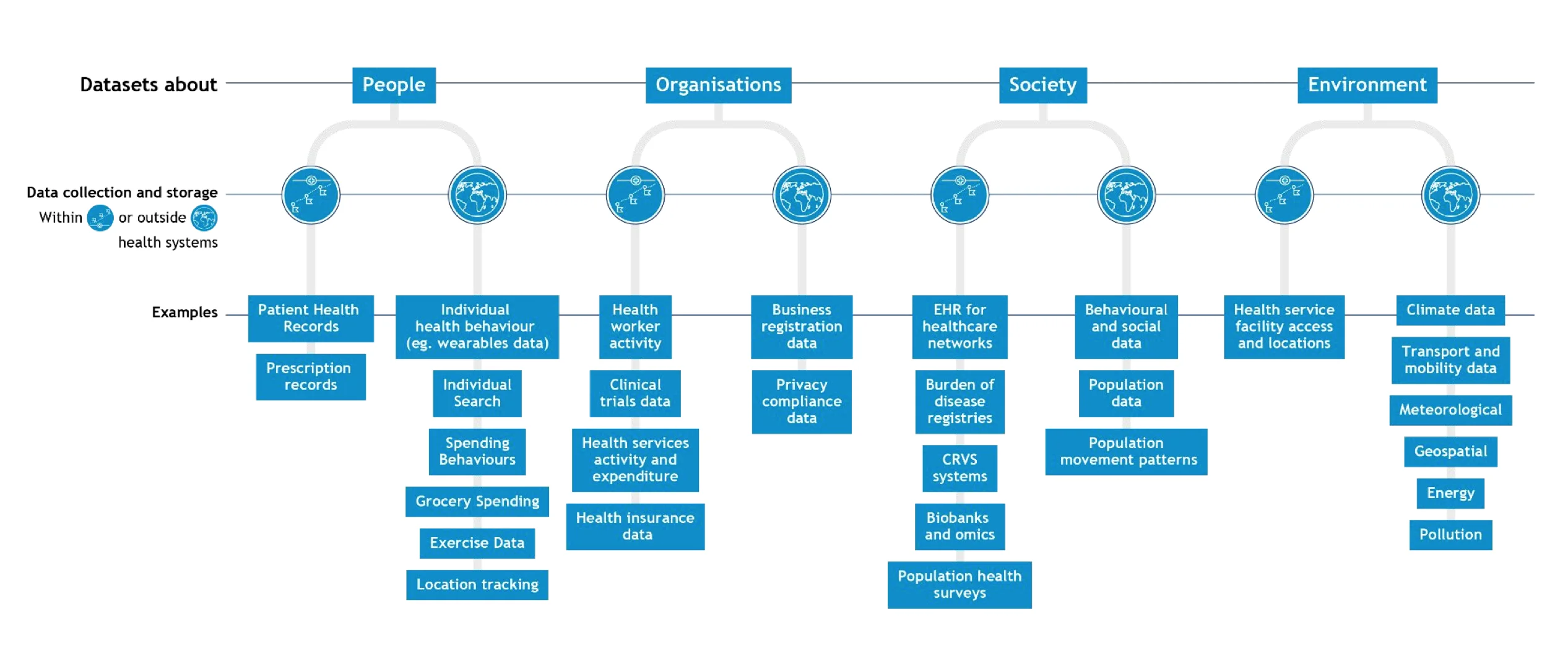
The various types and formats of healthcare data - Source: Health Data Governance Summit by WHO.
Data governance can establish data exchange standards, formats, and sharing policies, enabling seamless integration across different systems and providers.
This paves the way for an interoperable healthcare data system, which will enhance care coordination, reduce duplication of tests and procedures, and ensure comprehensive patient care.
Next, let’s check out the benefits of effective data governance in healthcare.
The benefits of data governance in healthcare #
Healthcare data can generate value with:
- Better healthcare decision-making: The core benefits of implementing a robust data governance program are improving data quality and enhancing decision-making. The World Economic Forum highlights that accurate and trustworthy data helps with disease control tasks, such as predicting the spread of illnesses, identifying infection clusters, and tracking the contacts of carriers.
- Cost optimization: Effective data governance reduces data duplication, streamlines operations, and automates workflows, leading to significant cost savings. For example, a hospital that centralizes its data management can reduce the costs associated with managing multiple fragmented systems, freeing up resources for patient care. It also reduces the costs and resources needed to find and compile the right information.
- Compliance assurance: Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations, such as HIPAA, is critical to avoiding fines and maintaining patient trust. Proper data governance ensures that all data handling practices comply with regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of breaches and protecting the organization’s reputation.
- Innovation and competitive advantage: Data governance enables healthcare organizations to leverage automation and AI to drive innovation. For instance, AI-assisted search and discovery can help you find the information you need quickly and at a glance. AI-powered analytics can identify patterns in patient data that lead to more personalized treatment plans, thereby improving patient outcomes.
Now, let’s explore the essential capabilities required for effective data governance.
How to implement data governance in healthcare: Essential capabilities #
To implement data governance effectively, healthcare organizations should look for the following essential capabilities:
- Data cataloging: An enterprise data catalog, powered by automated metadata harvesting, cross-platform semantic mapping, etc., acts as a centralized repository where healthcare organizations can easily discover, understand, and use relevant data.
- Metadata management: Effective metadata management captures, describes, and manages all types of metadata (clinical, operational, admin, and custom metadata). This makes it easier to find, use, and govern data. Meanwhile, automation – automatic update and sync of metadata changes across your data estate, automated profiling, etc. – is a crucial capability for ensuring data accuracy, compliance, and governance at scale.
- Data lineage: Understanding the flow of data through various healthcare systems is critical for tracking its origin, usage, and transformation. Healthcare organizations should look for granular data lineage mapping (with impact and root cause analysis) that’s actionable and automated.
- Access controls and security: Implementing granular access controls and security measures is vital for protecting sensitive data and ensuring regulatory compliance. Data governance solutions for healthcare should also support risk assessment and be aligned with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
- Data contracts:Data contracts establish clear agreements between data producers and consumers, outlining the expectations, responsibilities, and quality standards for data usage. As a result, everyone in your ecosystem is aligned, reducing the risk of data-related disputes and enhancing data reliability across the organization.
- AI-assisted policy creation: AI can streamline the creation of data governance policies by analyzing existing data, suggesting appropriate policies, and automating policy updates.
- Transparency center for data governance policies: A transparency center provides a top-down view of data governance policy coverage across your healthcare data estate. This allows you to monitor which policies are in place, where they are applied, and how effectively they are enforced.
- Real-time incident alerts: Real-time incident alerts notify relevant stakeholders about policy incidents and breaches as they happen (and not years later), prompting immediate action to mitigate risks. As a result, you can proactively prevent the escalation of issues that could lead to major operational and compliance challenges.
Data governance in healthcare: Set the stage for high-quality patient care #
Health data is a strategic asset, and strong data governance is crucial for making well-informed decisions and ensuring the highest quality of patient care. Data governance in healthcare is a standardized and structured approach to collecting, managing, analyzing, and sharing medical data transparently while adhering to ethical and regulatory standards.
Implementing data governance in healthcare is not just about compliance—it’s about enhancing patient care, improving operational efficiency, and driving innovation.
This article covers the need for data governance in healthcare, followed by benefits, and key capabilities in data governance solutions. Consider these as a starting point and set the stage for sustainable excellence, growth, and innovation.
Data governance in healthcare: Related reads #
- What is Data Governance? Its Importance, Principles & How to Get Started?
- Data Governance Framework — Examples, Templates, Standards, Best Practices & How to Create One?
- Data Governance and Compliance: An Act of Checks & Balances
- 7 Use Cases of Data Analytics in Hospitality Industry in 2024
- Data Governance and GDPR: A Comprehensive Guide to Achieving Regulatory Compliance


